Differentialgleichungen am Computer
Lösungen von Differentialgleichungen
Differentialgleichungen 1. Ordnung:
> eq1:=diff(y(t),t)=k*y(t);
> sol1:=dsolve(eq1,y(t));
![]()
![]()
Anfangswertproblem: y(0)=2
> eval(subs(t=0, y(0)=2, sol1));
![]()
> subs(_C2=2, sol1);
oder einfacher lösen wir die Diffe
![]()
rentialgleichung gleich als Anfangswertproblem
> sol1b:=dsolve({eq1, y(0)=2}, y(t));
![]()
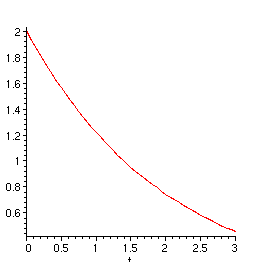
Setzen wir k=-0.5 und lassen wir die Lösungskurve zeichnen:
> sol1c:=subs(k=-0.5, sol1b);
![]()
> plot(sol1c, t=0..3);
rhs ... 'right hand side'
Plotting error, empty plot
> plot(rhs(sol1c), t=0..3);
Zur Kontrolle, ob eine zum Bsp. von Hand gerechneten Lösung wirklich Lösung der Differentialgleichung ist:
> eq2:=diff(y(x), x)=1+y(x)^2;
![]()
> y2:=tan(x+c);
![]()
> subs(y(x)=y2, eq2);
![]()
> eval(%);
![]()
Differentialgleichungen 2. Ordnung:
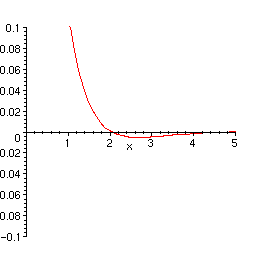
Dgl. 2. Ordnung mit konstanten Koeffizienten und lamda1 = lamda2
> eq3:=(D@@2)(y)(x)+3*D(y)(x)+9/4*y(x)=0;
![]()
> yp3:=dsolve({eq3,y(0)=1, D(y)(0)=-2},y(x));
![[Maple Math]](images/vorf5output13.gif)
> plot(rhs(yp3), x=0..5, y=-0.1..0.1);
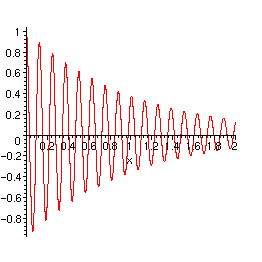
Charakteristische Gleichung besitzt konjugiert komplexe Lösungen
> eq4:=(D@@2)(y)(x)+2*D(y)(x)+2501*y(x)=0;
![]()
> yp4:=dsolve({eq4, y(0)=1, D(y)(0)=-1}, y(x));
![]()
> plot(rhs(yp4), x=0..2,numpoints=1000);
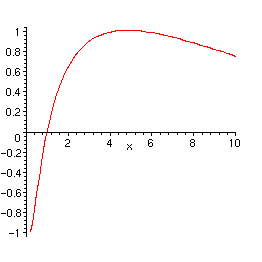
Eulersche Dgl.: Charakteristische Gleichung besitzt konjugiert komplexe Lösungen (0.10)
> eq5:=x^2*(D@@2)(y)(x)+x*D(y)(x)+y(x)=0;
![]()
> yp5:=dsolve({eq5, y(1)=0, D(y)(1)=1}, y(x));
![]()
> plot(rhs(yp5), x=0..10);
Zur Kontrolle, ob eine zum Bsp. von Hand gerechneten Lösung wirklich Lösung der Differentialgleichung ist: (0.1b)
> eq6:=(1-x)*diff(y(x), x,x)+x*diff(y(x),x)-y(x)=0;
![[Maple Math]](images/vorf5output21.gif)
> y6:=exp(x)+x;
![]()
> subs(y(x)=y6, eq6);
![[Maple Math]](images/vorf5output23.gif)
> simplify(eval(%));
![]()
Inhomogene Dgl:
> Ly7:=diff(y(x),x,x)-4*diff(y(x),x)+3*y(x);
![[Maple Math]](images/vorf5output25.gif)
> g7:=10*exp(-2*x);
![]()
> sol7:=dsolve({Ly7=g7,y(0)=1, D(y)(0)=-3},y(x));
![]()
Lineare Dgln. höherer Ordnung:
Wronskideterminante:
> eq8:=(D@@4)(y)(x)-5*(D@@2)(y)(x) + 4*y(x)=0;
![]()
> dsolve(eq8, y(x));
![]()
Basis von Lösungen:
> with(linalg):
> B8:=[exp(x), exp(2*x), exp(-2*x), exp(-x)];
Warning, new definition for norm
Warning, new definition for trace
![]()
> A8:=matrix([B8, diff(B8,x), diff(B8,x,x), diff(B8,x,x,x)]);
![[Maple Math]](images/vorf5output31.gif)
> W:=det(A8);
![]()
> W:=simplify(%);
![]()
Systeme von Differentialgleichungen:
> sys1:=D(z1)(t)=-3*z1(t)+z2(t),D(z2)(t)=z1(t)-3*z2(t);
![]()
> dsolve({sys1}, {z1(t), z2(t)});
![]()
![]()
> dsolve({sys1, z1(0)=1, z2(0)=5}, {z1(t), z2(t)});
![]()
> with(linalg):
> A1:=matrix(2,2,[-3,1,1,-3]);
![[Maple Math]](images/vorf5output38.gif)
> eigA1:=eigenvects(A1);
![]()
> lamda1:=eigA1[1][1];
![]()
> x11:=eigA1[1][3][1];
![]()
> lamda2:=eigA1[2][1];
![]()
> x12:=eigA1[2][3][1];
![]()
> sol1:=_C1*x11*exp(lamda1*t)+_C2*x12*exp(lamda2*t);
![]()
> sol1:=evalm(%);
![]()
>
Phasenportraits
Phasenportäts:
> with(share); with(ODE);
![]()
Share Library: ODE
Author: Daniel Schwalbe.
Description: package for solving ODE's numerically and plottingtheir solutions
![]()
uneigentlicher Knoten im Ursprung:
> eq1:=(t,y1,y2) ->-3*y1+y2;
![]()
> eq2:=(t,y1,y2) ->y1-3*y2;
![]()
> inits:=[1,1],[-1,1],[-1,-1],[1,-1],[1,3],[-3,-1],[-1,-3],[3,1],[0,2],[-2,0],[0,-2],[2,0]:
> phaseplot([eq1,eq2],-3..3,-2..2,{inits},numsteps=200);
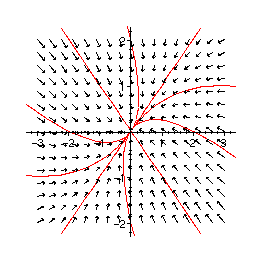
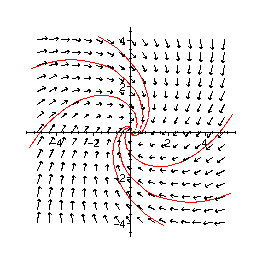
Sattelpunkt:
> sys2:=D(y1)(t)=2*y1(t)-4*y2(t),D(y2)(t)=y1(t)-3*y2(t);
![]()
> sol2:=dsolve({sys2},{y1(t),y2(t)});
![]()
![]()
>
> eq21:=(t,y1,y2) ->2*y1-4*y2;
![]()
> eq22:=(t,y1,y2) ->y1-3*y2;
![]()
> inits:=[1,1],[-1,-1],[4,1],[-4,-1],[0,1],[0,-1],[0,2],[0,-2],[2,1],[-2,-1],[3,2],[-3,-2];
![]()
![]()
> phaseplot([eq21,eq22], -5..5, -4..4, {inits}, numsteps=200);
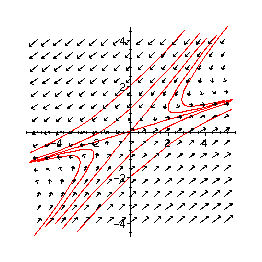
'Center'
> sys3:=D(y1)(t)=y2(t), D(y2)(t)=-4*y1(t);
![]()
> sol3:=dsolve({sys3},{y1(t),y2(t)});
![]()
![]()
> eq31:=(t,y1,y2) -> y2;
![]()
> eq32:=(t,y1,y2) -> -4*y1;
![]()
> inits:=[0,1], [0,2], [0,3];
![]()
> phaseplot([eq31,eq32], -6..6, -4..4, {inits}, numsteps=200);
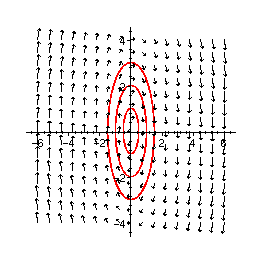
Strudelpunkt:
> sys4:=D(y1)(t)=-y1(t)+y2(t), D(y2)(t)=-y1(t)-y2(t);
![]()
> sol4:=dsolve({sys4},{y1(t),y2(t)});
>
![]()
![]()
> eq41:=(t,y1,y2) ->-y1+y2;
![]()
> eq42:=(t,y1,y2) ->-y1-y2;
![]()
> inits1:=[1,0],[2,0],[3,0],[-1,0],[-2,0],[-3,0];
![]()
> phaseplot([eq41,eq42], -5..5, -4..4, {inits1}, numsteps=200);
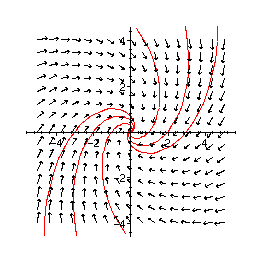
> inits2:=[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[0,-1],[0,-2],[0,-3];
![]()
> phaseplot([eq41,eq42], -5..5, -4..4, {inits2}, numsteps=200);
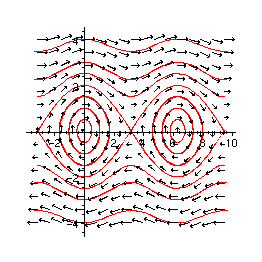
> eq51:=(t,y1,y2) -> y2;
![]()
> eq52:=(t,y1,y2) -> -sin(y1);
![]()
> inits:=[0,1/2],[0,1],[0,3/2],[0,2],[0,5/2],[0,3],[0,4],[0,-5/2],[0,-3],[0,-4],[2*Pi,1/2],[2*Pi,1],[2*Pi,3/2],[2*Pi,2];
![]()
![]()
> phaseplot([eq51,eq52], -Pi..3*Pi, -4..4, {inits}, numsteps=200);
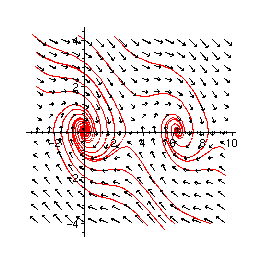
Damping
> eq61:=(t,y1,y2) -> y2;
![]()
> eq62:=(t,y1,y2) -> -sin(y1)-1/2*y2;
![]()
> inits:=[0,1/2],[0,1],[0,3/2],[0,2],[0,5/2],[0,3],[0,4],[0,-1],[0,-3/2],[0,-2],[2*Pi,1/2],[2*Pi,-1],[2*Pi,-3/2];
![]()
![]()
> phaseplot([eq61,eq62], -Pi..3*Pi, -4..4, {inits}, numsteps=200);
>
>
>
Potenzreihenansätze
Potenzreihen:
> series(exp(x),x);
![]()
> series (ln(1+x),x,10);
![]()
Entwicklungsmitte Pi/2
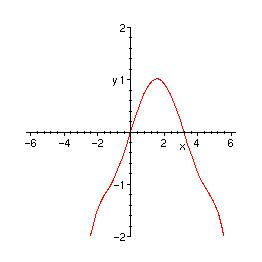
> f:=series(sin(x),x=Pi/2,8);
![]()
Um Graphen zu zeichnen ist es nötig zuerst den Fehlerterm O(x^n) zu eliminieren
> p:=convert(f,polynom);
![]()
> plot(p,x=-2*Pi..2*Pi,y=-2..2);
> f:=series(sin(x),x=Pi/2,64):
> p:=convert(f,polynom):
> plot(p,x=-5*Pi..5*Pi,y=-1..1);
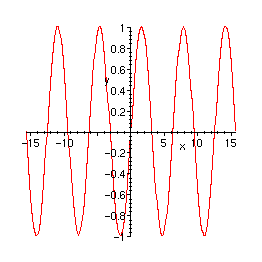
Lösen von Differentialgleichungen mittels Potenzreihenansatz:
> eq1:=D(y)(x)+2*x*y(x)=0;
![]()
> dsolve(eq1, y(x), series);
![]()
Für ein Anfangswertproblem:
> dsolve({eq1, y(0)=1}, y(x), series);
![]()
> Order:=12;
![]()
> sol1:=dsolve(eq1,y(x),series);
![]()
![]()
> yp1:=subs(y(0)=1, sol1);
![]()
> yp1:=convert(rhs(yp1),polynom);
![]()
> plot(yp1,x=-1..1);
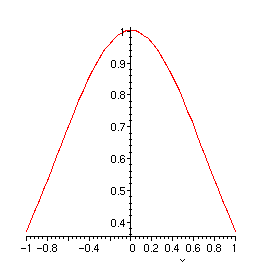
Orthogonale Polynome:
Legendre Polynome:
> with(orthopoly);
![]()
P(n,x) erzeugt das n-te Legendre Polynom:
> P(2,x);
![]()
> P(3,x);
![]()
> P(4,x);
![]()
Oder wir schreiben eine eigene Prozedur, um diese Polynome zu erzeugen
> Legendre:=proc(n)
> if n=0
> then 1
> else 1/(2^n*n!)*diff((x^2-1)^n,x$n)
> fi;
> end:
> Legendre(2);
![]()
> Legendre(3);
![]()
> simplify(%);
![]()
> S:=seq(simplify(Legendre(n)), n=0..4);
![]()
> plot({S}, x=-1.5..1.5, y=-1..1);
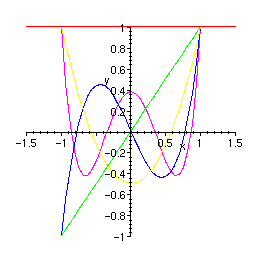
> S:=seq(simplify(Legendre(n)), n=10..15);
> plot({S}, x=-1.5..1.5, y=-1..1,numpoints=1500);
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
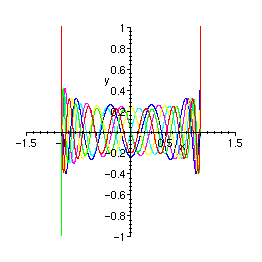
> eq2:=(1-x^2)*(D@@2)(y)(x)-2*x*D(y)(x)+6*y(x)=0;
![]()
> P2:=dsolve({eq2, y(-1)=1,y(1)=1},y(x));
![]()
> eq3:=(1-x^2)*(D@@2)(y)(x)-2*x*D(y)(x)+12*y(x)=0;
![]()
> P3:=dsolve({eq3,y(-1)=-1,y(1)=1},y(x));
![]()
Bessel Funktion:
> J0:=series(BesselJ(0,x),x=0,11);
![]()
> J0:=convert(J0,polynom);
![]()
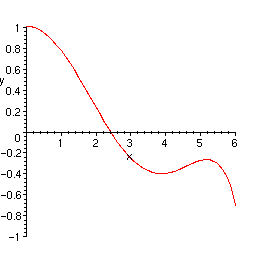
> plot(J0,x=0..6,y=-1..1);
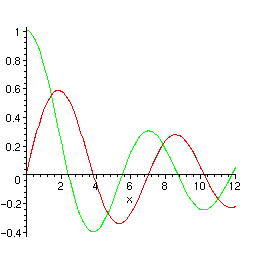
> plot({BesselJ(0,x),BesselJ(1,x)},x=0..12);
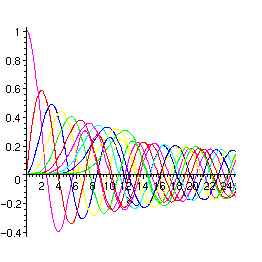
> S:=seq(BesselJ(n,x), n=0..10);
> plot({S}, x=0..25);
![]()
![]()
> eq4:=x*(D@@2)(y)(x)+D(y)(x)+x*y(x)=0;
![]()
> Order:=11;
![]()
> dsolve({eq4,y(0)=1,D(y)(0)=0},y(x),series);
![]()
> evalf(%);
![]()
![]()
>
>